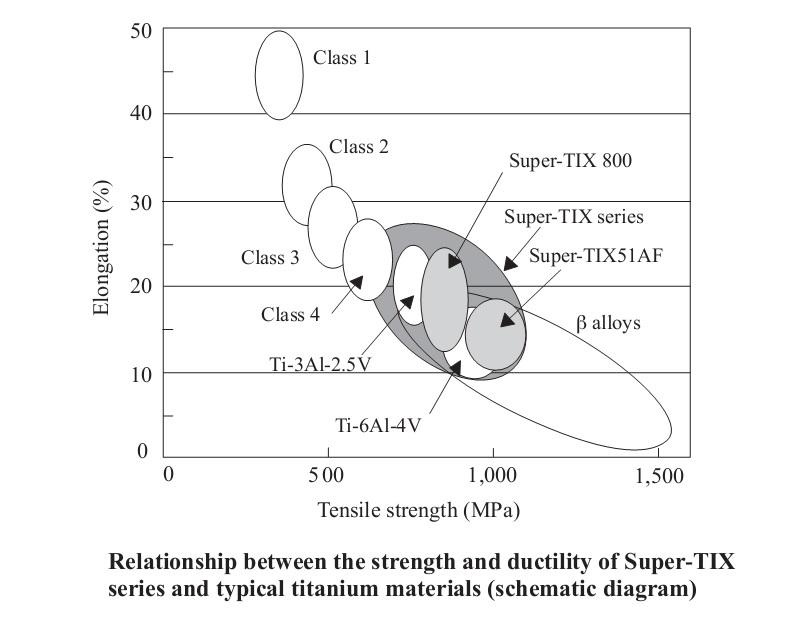
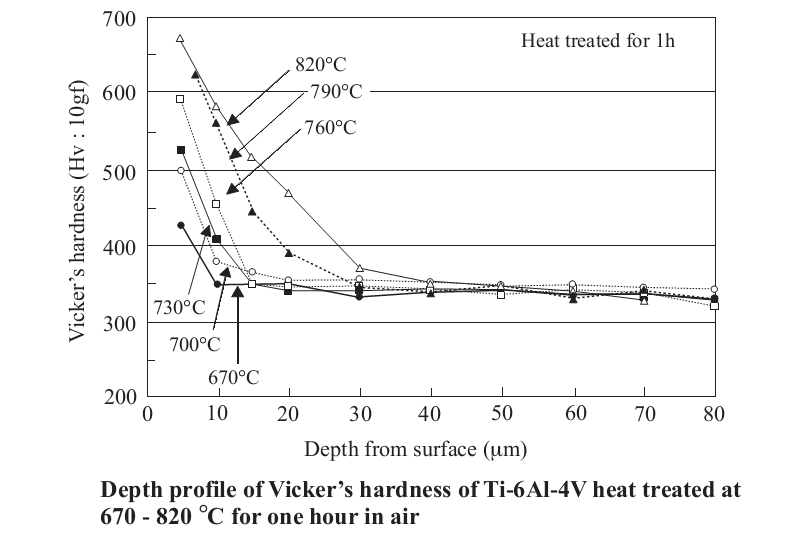
Titanium
| 3.0AL 2.5V | Titanium 6-2-4-2 | Titanium 6-2-4-6 | 6-4 | 6-6-2 |
| 6AL 2Sn 4Zr 2Mo | 6AL-4V | 6AL-4V S | Comm | CP |
Because of their excellent corrosion resistance and high specific strength (strength/density), titanium and its alloys have been widely used for chemical, electric power, and aerospace industries as major metal materials by taking advantage of their characteristics. On the other hand, their applications to automobile industry have been lim-ited except for racing cars and special-purpose cars because of their high cost despite the strong interest shown in titanium materials by the industry in terms of lightweight, fuel efficiency, and performances.
In recent years, however, titanium and its alloys have come to be actively used for various parts of the general mass-produced cars due to the following factors:
- The demand for lightweight parts has become increasingly strict for the prevention of global warming though reduction of CO2 emission;
- Remarkable progress has been made in the development of tech-nology for the manufacture of low-cost titanium; and
- The appearance and fashionableness peculiar to titanium have come to appeal to the public.